What is Data: Its Types, Usage and Storage

Data is
a collection of raw facts from which conclusions might be drawn. Organizations
process data to derive the information required for their day-today operations.
Storage is a repository that enables users to persistently store and retrieve
this digital data.
Today, data can be converted into more convenient forms, such as an e-mail message, an e-book, a digital image, or a digital movie. This data can be generated using a computer and stored as strings of binary numbers (0s and 1s).Data in this form is called digital data and is accessible by the user only after a computer processes it.
Some of the factors that have contributed to the growth of digital data are as follows:
1.
Increase in data-processing capabilities
2.
Lower cost of digital storage
3.
Affordable and faster communication technology
4.
Proliferation of applications and smart devices
Inexpensive and easier ways to create, collect, and store all types of data, coupled with increasing individual and business needs, have led to accelerated data growth, popularly termed data explosion.
The importance and value of data vary with time. Typically, recent data which has higher usage is stored on faster and more expensive storage. As it ages, it may be moved to slower, less expensive but reliable storage.
Data can vary in criticality and might require special handling. This requires high-performance and high-capacity storage devices with enhanced security and compliance that can retain data for a long period.
A DATA CENTER is a facility that contains
information storage and other physical information technology (IT) resources
for computing, networking, and storing information.
Virtualization optimizes resource utilization and eases resource management. Organizations incorporate virtualization in their data centers to transform them into virtualized data centers (VDCs).
Cloud computing, which represents a fundamental shift in how IT is built, managed, and provided, further reduces information storage and management complexity and IT resource provisioning time. Through cloud computing, an organization can rapidly deploy applications where the underlying storage capability can scale-up and scale-down, based on the business requirements.
Types of Data
Data
can be classified as structured or unstructured based on how it is stored
and managed.

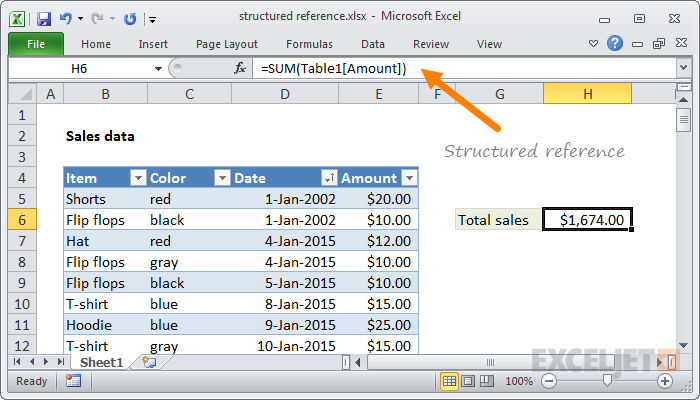
Structured data is organized in rows and columns in a rigidly defined format so that applications can retrieve and process it efficiently. Structured data is typically stored using a Database Management System (DBMS).
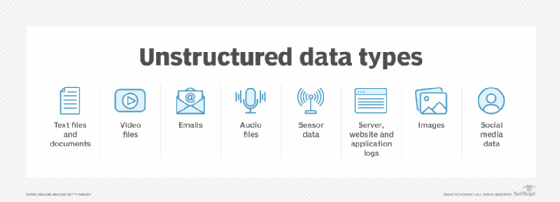
Data is unstructured if its elements cannot be stored in rows and columns, which makes it difficult to query and retrieve by applications. For example, data that are stored in various forms such as sticky notes, e-mail messages, business cards, or even digital format files, such as .doc, .txt, and .pdf. Due to its unstructured nature, it is difficult to retrieve this data using a traditional relationship management application.
Big Data
Big data is
a new and evolving concept, which refers to data sets whose sizes are beyond
the capability of commonly used software tools to capture, store, manage, and
process within acceptable time limits. It includes both structured and
unstructured data generated by a variety of sources.
Significant
opportunities exist to extract value from big data. The big data ecosystem
consists of the following:
1.
Devices that
collect data from multiple locations and also generate new data about this data
(metadata).
2.
Data collectors
who gather data from devices and users.
3.
Data
aggregators that compile the collected data to extract meaningful information
4. Data users and buyers who benefit from the information collected and aggregated by others in the data value chain.
Information
Data,
whether structured or unstructured, does not fulfil any purpose for individuals
or businesses unless it is presented in a meaningful form. Information is
the intelligence and knowledge derived from data.
Storage
Data
created by individuals or businesses must be stored so that it is easily accessible
for further processing. In a computing environment, devices designed for
storing data are termed storage devices or simply storage.
The type of storage used varies based on the type of data and the rate at which
it is created and used.

Written by: Sameer




Good post. This definitely includes something that holds more value and we can learn from
ReplyDeleteThanks
Fastractor